Eco-Friendly BioGel Moz Bait Delivery for Efficient Attracting & Killing Mechanism of Aedes Mosquito

Assoc. Prof. Dr. Nur Faeza Abu Kassim
Ts. ChM. Dr. Sumiyyah Sabar
Noor Muokhni Ayub
Ranjitha Sambanthan
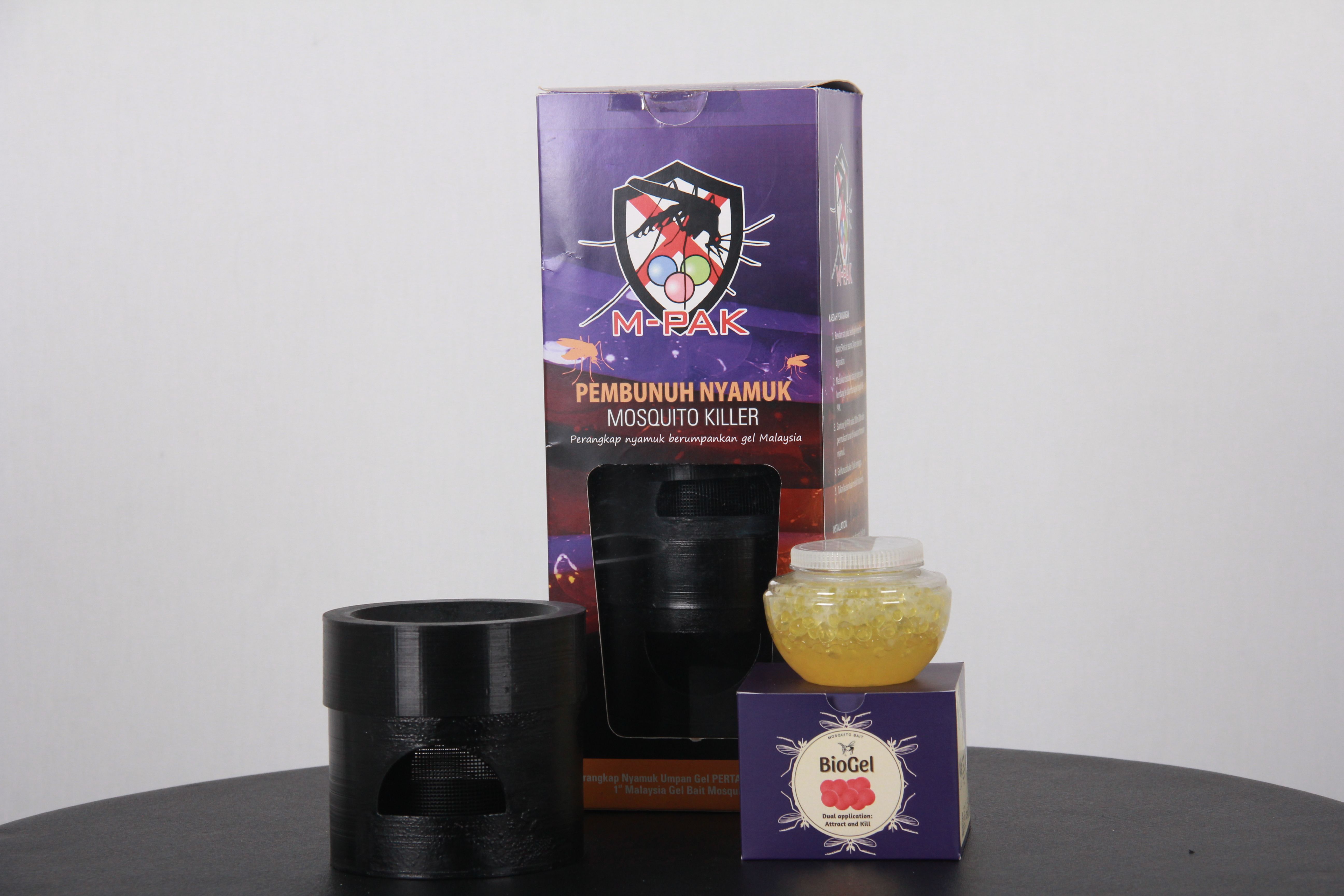
BioGel Moz are biopolymer-based hydrogel beads developed for a sustainable, durable, and safer mosquito bait. It is designed using sugar bait technology as an innovative strategy for controlling mosquitoes in urban and rural environments. This invention is a cost-effective and highly marketable product for controlling mosquito-borne diseases. BioGel Moz is in line with Malaysia's priority areas of KEGA-12 on green economy, SDG-3 focusing on tropical disease, WKB 2030 and the 2030 Agenda.
Problem Statement
- The cumulative number of dengue cases reported in Malaysia from January until November 2019 was 110,399 cases, including 156 deaths. The numbers are higher compared to the reported cases during the same period in 2018.
- Traditional mosquito control pesticides are formulated as a spray containing organophosphates or synthetic pyrethroids.
- However, the methods provide poor mosquito control and pose hazards to human health and the environment.
- It has been estimated that most pesticides used are lost to the environment, and only less than 1% remain on target. This low effectiveness contributes to serious environmental pollution.
- Besides, the use of synthetic polymers as a baiting tool also contributes to the environmental problem due to their toxicity, bioaccumulation, and non-biodegradability.
- Therefore, efforts should be taken to reduce waste, production costs, and environmental pollution associated with pest control while also extending the duration of the pesticide activity.
Novelty and Inventiveness
- A strategic control program that integrates the application of biological and chemical processes to control the targeted vector.
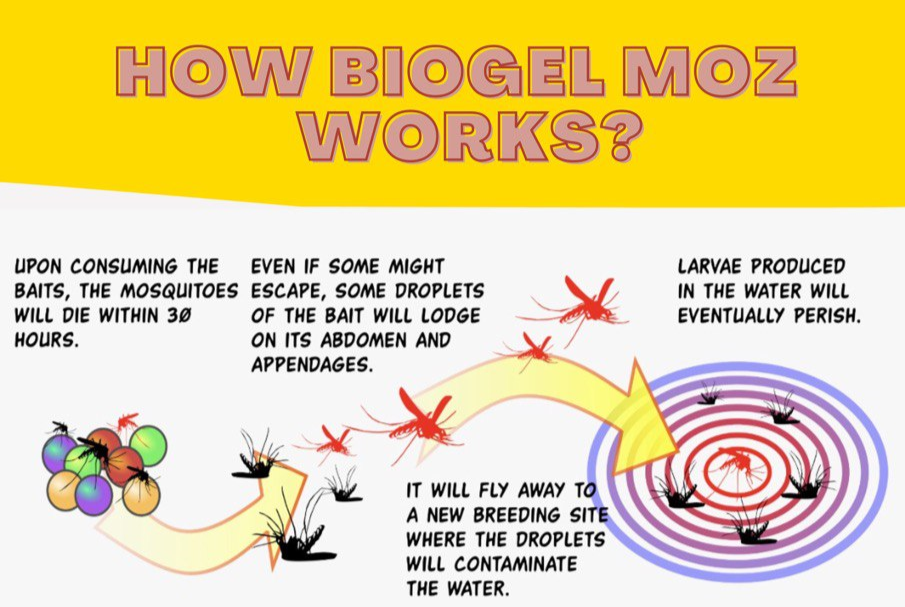
- The biopolymer hydrogel beads are made of sweet botanical scents as attractants to the vectors and blended with a tiny amount of biocide.
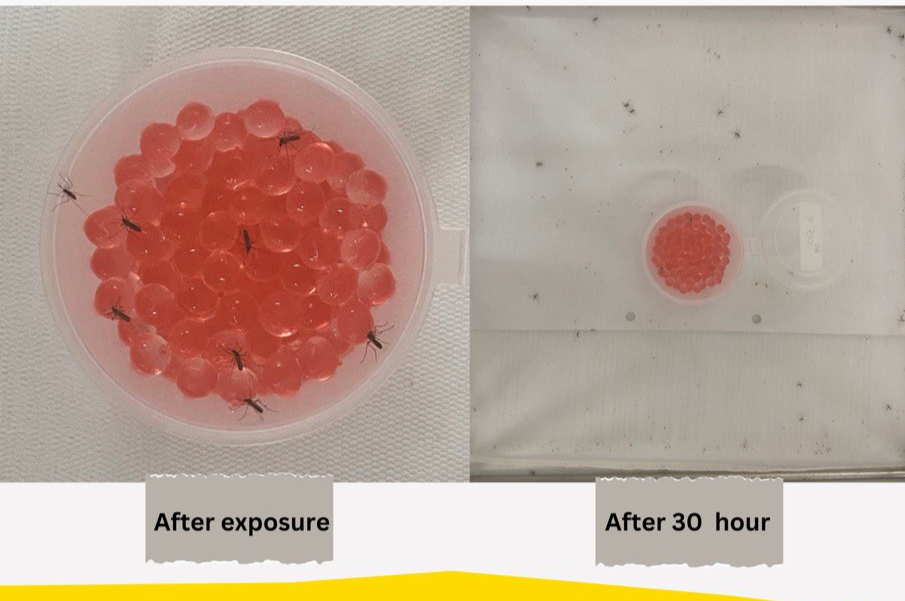
- The vectors that eat the bait will show a sub-lethal effect and die within 30 hours (slow killing).
- After in contact with the hydrogel beads, the vectors will spread the catalyst larvicide into new breeding sites - “vectors will kill their friends”.
- The efficiency of BioGel Moz demonstrates that it can be used as a slow-release pesticide carrier that is safe and sustainable to be implemented in the health sectors.
Applicability and Benefits
BioGel Moz has broad prospects for applications in the health sectors. The benefits are as follows:
- The biopolymer hydrogel beads offer an effective / novel delivery system for liquid baits with low biocide concentrations to control mosquitoes.
- It provides economically feasible, better public health protection and an environmentally safer alternative.
- It is simple, low-cost, durable, safe and sustainable to be applied indoors and outdoors.
- The innovative control strategy targeted specific vectors based on their diet – the “attract and kill strategy”.
- BioGel Moz bait is suitable for developed and open urban areas. Each bait is effective to kill adult mosquitoes and its larvae through its double action application within 400M square area.
Research Achievement
- 1 Research Contract: MozFree Sdn. Bhd.
- 3 ISI Publication: International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, The Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Viedicine and PublicHealth, Journal of American Mosquito Control AssoCiation.
- 2 Patent Granted: Patent granted (100% USM), Grant Number: MY-195446-A, Date of Granted: 22 January 2023; Patent filed and Pending (100% USM), Reference Number: USM/CIC/PT/HA/2022/023, Date of Filling: 14 September 2022.
- 6 Funding: Geran Dana Inovast Awal (DiA-USM) - RM 24,000; Research University Grant (RUI-USM) - RM 64,000; MozFree (M) Sdn. Bhd. - RM5000; The California Academy of Sciences, USA. USD5OK; FRGS (KPT) - RM148,060.00; Penang State Government - RM130K.
- 12 Talent Development: 2 Master, 10 FYP.
Commercialization Potential And Industrial Partner
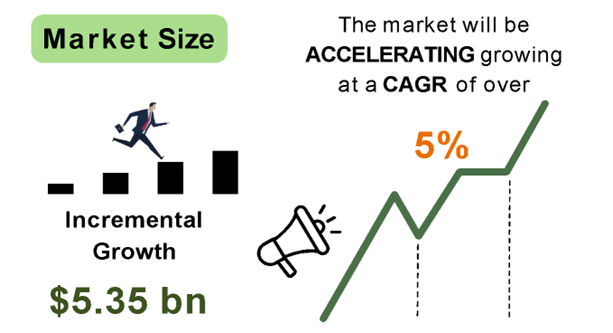
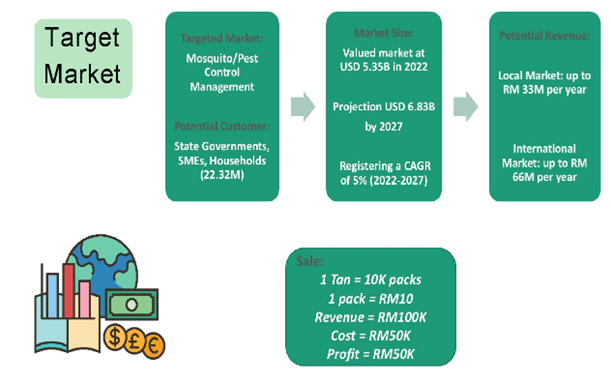
- The financial costs associated with current preventive activities due to mosquitoes and other pest-related diseases are over US$176 million as of 2021.
- The use of local sugar-based vector control can promote the development of local mosquito and pest prevention industries with regional and global markets.
Status of Invention
Technology Readiness Level 8 - Developed and proven in an operational environment.
Intellectual Property Status
- Malaysian Patent Application Granted, Grant Number: MY-195446-A, Date of Granted: 22/01/2023.
- Patent filed and Pending, Reference Number: USM/CIC/PT/HA/2022/023, Date of Filling: 14/09/2022.
Impact of Innovation
- Society: With the burden of mosquito-borne disease severely impacting communities internationally, effective mosquito management tools will directly improve the health and well-being of society.
- Academia: The proposed study will establish a foundation for future research opportunities among the international mosquito research community to control vectors.
- Government: The local use of sugar-based vector control can help reduce dengue occurrence and the financial costs associated with current preventive activities, which are at US$176 million as of 2021.
- Industry: Discovering that sugar bait technology offers mosquito control tools can promote the development of local mosquito prevention industries with regional and global markets.
- Environment: This implementation can reduce the undesirable environmental effect by eliminating the accumulation of synthetic compounds (e.g., acrylamides), which are associated with the first objectives of National Policy on the Environment (DASN); to attain a clean environment, safe, healthy and productive environment for present and future generations.